11. Quiz: Incremental Mean
Quiz: Incremental Mean
In the previous video, we learned about an algorithm that can keep a running estimate of the mean of a sequence of numbers (x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n). The algorithm looked at each number in the sequence in order, and successively updated the mean \mu.
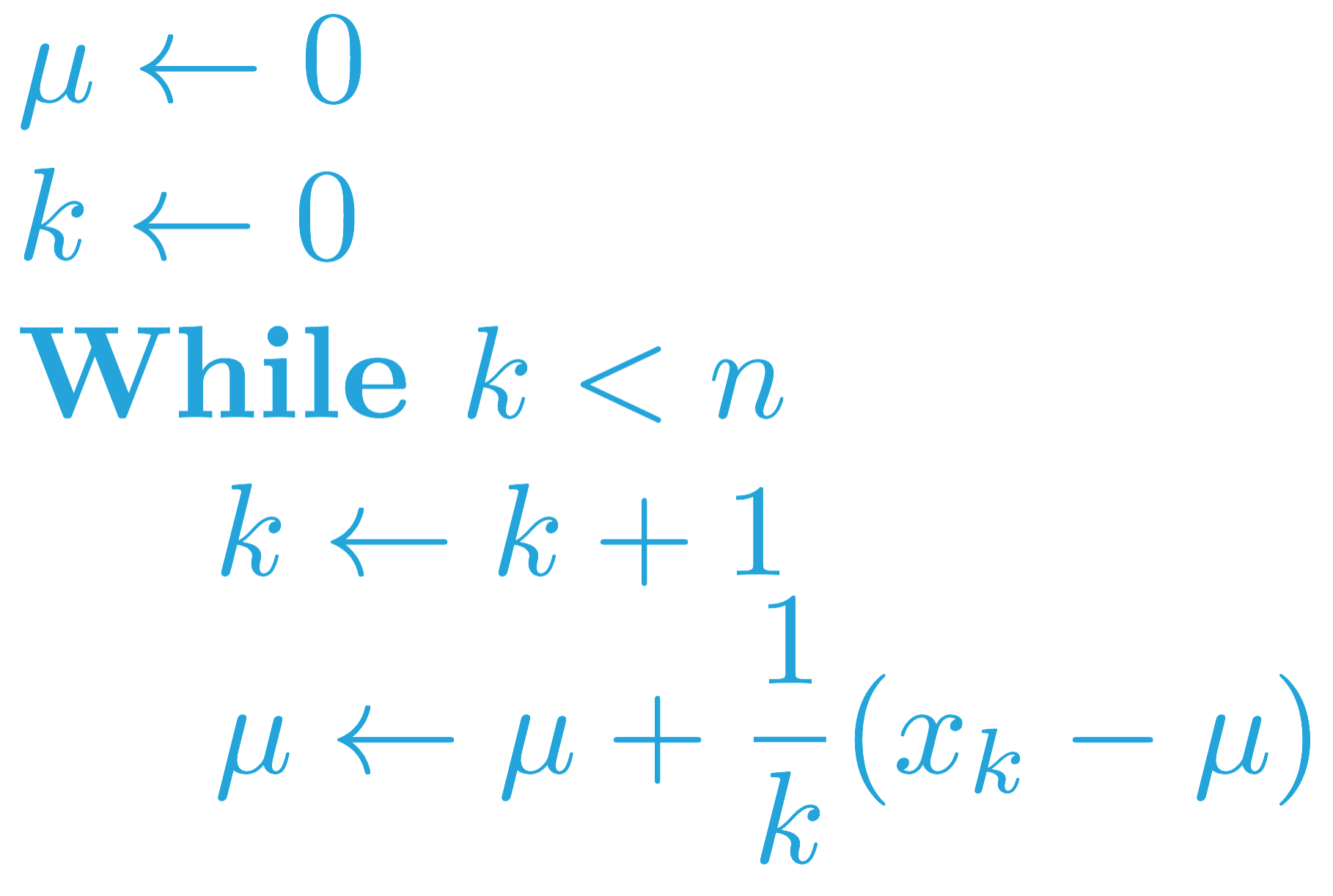
Use the pseudocode to complete the running_mean function below. Your function should accept a list of numbers x as input. It should return a list mean_values, where mean_values[k] is the mean of x[:k+1].
Note: Pay careful attention to indexing! Here, x_k corresponds to x[k-1] (so x_1 = x[0], x_2 = x[1], etc).
Use the [ Test Run ] button to check the accuracy of your code. When you are ready to move on to the next concept, click on [ Submit Answer ].
Start Quiz: